- What is a Sitemap?
- Types of Sitemaps
- What is an XML Sitemap?
- Importance of XML Sitemap in SEO
- What are the Benefits of XML Sitemaps?
- What is an HTML Sitemap?
- What is the Importance of HTML Sitemaps in SEO?
- What are the Benefits of HTML Sitemaps?
- How Sitemaps Affect Crawling and Indexing?
- What Are the XML Sitemaps Best Practices?
- What Are the HTML Sitemaps Best Practices?
- What Major Issues Businesses Faces with Sitemap?
- Important Points to Consider in XML Sitemap
- Conclusion
- FAQs
You’ve likely encountered various types of maps, such as road maps guiding us to destinations, treasure maps leading to hidden treasures, and geographical maps depicting the Earth’s surface, among others.
But have you ever heard about the term “website sitemaps”?
Sitemaps aren’t like regular maps; they are complex to understand and not fun, trust me! However, once you know how to read sitemaps, they can provide a path to higher ranking and more website traffic.
So, if you want to learn about website sitemaps, this blog covers you.
Without wasting much of your time, let’s get started.
What is a Sitemap?
A sitemap acts like a detailed framework of your website, showcasing crucial details about its pages, URLs, videos, and other files. Also, it plays an important role in guiding SEO crawlers to effectively recognize and organize these elements, prioritizing them based on their relevance and significance.
Types of Sitemaps

Now that you know the basic definition of sitemaps, let’s understand the different types of sitemaps. The sitemaps can be categorized into two main types:
- XML Sitemaps: This sitemap is structured in a format easily interpreted by search engine crawlers.
- HTML Sitemaps: This sitemap resembles standard web pages and guides users in navigating the site efficiently.
What is an XML Sitemap?
If you type mamaearth.in/sitemap.xml and hit enter……
Boom! You just found out all the important URLs for the website!
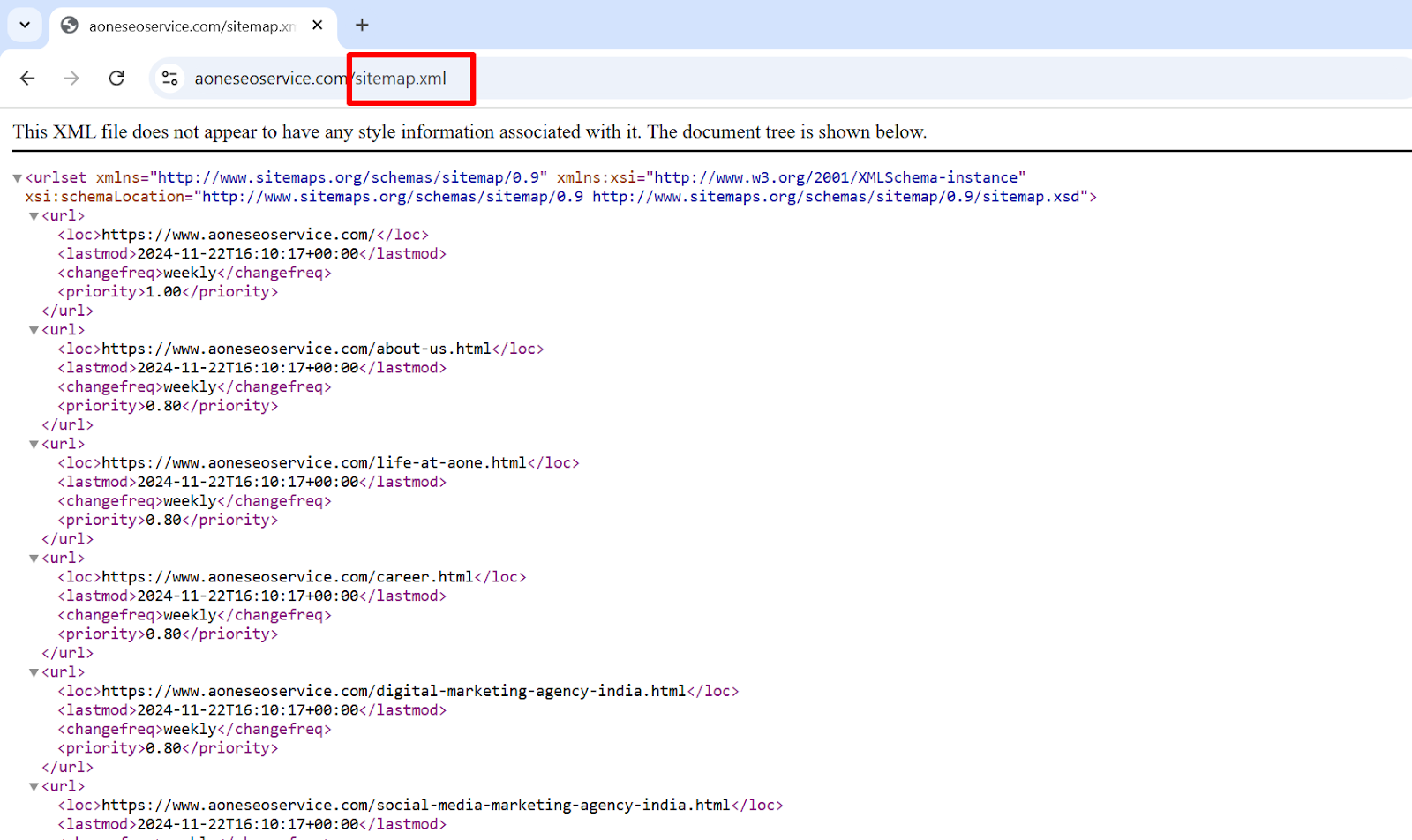
XML sitemap is a widely used format favored by search engines like Google. XML sitemaps list all the URLs you wish to have indexed and offer critical data for a website SEO audit, such as the ‘lastmod‘ attribute for updates and the ‘hreflang’ attribute for localization.

XML sitemaps are particularly beneficial for large websites. However, sites with extensive archives or newly launched sites with limited backlinks can also enjoy the perks of XML sitemaps.
Importance of XML Sitemap in SEO

After understanding about XML sitemap, let’s delve into why it holds significance in SEO.
XML sitemaps are vital in SEO by enhancing a website’s visibility and indexing efficiency. XML sitemaps also assist in identifying broken links during routine audits, which improves user experience and SEO performance. Here’s why it is important:
Facilitates Search Engine Crawling
XML sitemaps offer search engines a clear roadmap of all the URLs on your site, ensuring none of your webpages are overlooked during crawling, especially those that are deeply nested or lack backlinks.
Improves Indexing
By listing all relevant pages, an XML sitemap increases the chances of your content being indexed by search engines, even if your website is new or lacks an extensive link structure.
Provides Metadata
Sitemaps are important for SEO as they provide valuable metadata like the ‘lastmod’ attribute (indicating the last update), the ‘hreflang’ attribute (for localized versions of URLs), and the ‘changefreq’ and ‘priority’ tags (helping prioritize contents for crawlers).
Beneficial for Huge or Complex Websites
XML sitemaps ensure all critical pages remain accessible to search engines, especially for sites with vast archives or frequently adding new content.
Improves Crawl Budget Efficiency
XML sitemaps help search engines allocate their crawl budgets wisely by directing attention to high-priority pages, improving indexing speed and accuracy.
What are the Benefits of XML Sitemaps?
After understanding the importance of XML sitemap in SEO, let us look at some of the benefits of XML sitemaps.
Better Priority Management
Sitemaps help you define the importance of specific pages using priority tags, guiding search engines to focus on key content.
Facilitation of International SEO
By including ‘hreflang’ attributes, XML sitemaps help search engines understand the local versions of your content for different regions and languages.
Timely Updates
The ‘lastmod’ attribute informs search engines about recent updates, encouraging them to re-crawl updated content.
Boost for New Websites
Websites with limited or fewer backlinks and XML sitemaps ensure search engines can find and index their pages.
Improved User Experience
While primarily for search engines, they indirectly boost user experience by helping search engines better match relevant content with search queries.
Sitemaps in a Website SEO Audit
Sitemaps play a crucial role in a website SEO audit. They help ensure that all URLs are accounted for, identify broken links, and confirm that the correct HTTP status codes are returned. These checks ensure an optimized crawling process and a well-maintained website. Broken links discovered via sitemaps can be addressed using 301 redirects to ensure seamless navigation and preserve SEO equity.
What is an HTML Sitemap?

Now that you have comprehensively understood XML sitemaps let’s focus on HTML sitemaps.
In contrast, an HTML sitemap is a webpage that is accessible to visitors, containing a list of clickable links to all the website’s pages. While considered a somewhat outdated approach for sitemaps, it still remains valuable, particularly for large websites.
As mentioned above, HTML sitemaps might be considered outdated. However, Google still supports using them because a structured list of links helps the search engine better comprehend the site’s hierarchy. Therefore, it is easier to prioritize and index content effectively.
What is the Importance of HTML Sitemaps in SEO?
Like XML sitemap, HTML sitemap plays a crucial role in SEO by improving user navigation and search engine understanding of a website’s structure.
Here’s why HTML sitemaps are important in SEO:
Improved User Experience
HTML sitemaps provide visitors with a clear and accessible overview of a website’s pages, making it easier to look for specific content, especially on large or complex sites.
Improved Crawlability
Like XML, HTML sitemaps also improve crawlability by providing search engines an alternative path to discover and navigate web pages, helping index pages that might be overlooked.
Content Prioritization
HTML sitemaps help search engines identify the most important pages by presenting a hierarchical structure, influencing their indexing and ranking priorities.
Contextual Relevance
HTML sitemaps provide context by categorizing and organizing links logically, making it easier for search engines to understand relationships between pages.
Better Indexation for Older Content
Older, evergreen content can be surfaced more easily for search engines and users via an HTML sitemap, keeping it relevant and accessible.
What are the Benefits of HTML Sitemaps?
HTML sitemaps are highly beneficial today. Some of them include:
Improved User Navigation
HTML sitemaps offer a clear, organized list of links to all important pages on the website, making it easier for users to find specific content.
Support for Orphan Pages
HTML sitemaps make sure that orphan pages, pages without any links from other parts of the website, are still discoverable by search engines, increasing the chances of those pages being indexed.
SEO for Big Websites
For websites with many pages, an HTML sitemap acts as a directory, guiding users and search engines to key content, helping them navigate more efficiently.
User-Friendly Interface
HTML sitemaps are not just designed for search engines but for human visitors as well. They offer an easy way to browse and find content without relying on a search function, improving the overall user experience.
Boosts Internal Linking
Creating an HTML sitemap often leads to better internal linking by providing a centralized structure and improving the SEO of lesser-known or lower-ranking pages on your site.
Since you have a clear understanding of HTML sitemaps, let’s move on and explore how sitemaps impact crawling and indexing issues.
How Sitemaps Affect Crawling and Indexing?
As mentioned already, sitemaps play a crucial role in the crawling and indexing process by guiding search engine spiders to discover and categorize all the pages on a website.
Sitemaps play a vital role in a website SEO audit by guiding search engines to crawl and index URLs. During this process, HTTP status codes like 200 (OK), 301 (Redirect), and 404 (Not Found) indicate the status of each URL. Ensuring all sitemap URLs return proper status codes improves crawl efficiency and eliminates broken link issues, enhancing overall SEO performance. HTTP status codes not only indicate page functionality but also signal to search engines how to handle URLs, whether it’s indexing, redirecting, or ignoring them.
By providing a structured list of URLs, sitemaps ensure that search engines can access both visible and hidden pages, particularly those deep within the site or lacking direct internal links.
Crawling: Search engines use sitemaps to efficiently navigate a website, helping them find crawl pages that might otherwise be missed.
Indexing: After the pages are crawled, sitemaps guide search engines in determining the most relevant content to index. They help search engines understand the website’s structure, prioritize critical pages, and avoid indexing duplicate or irrelevant content.
Overall, sitemaps streamline the crawling process and improve indexing, positively affecting a site’s SEO performance and visibility in search results.
Identifying Broken Links with Sitemaps
Broken links, often referred to as “dead-end roads” in the digital landscape, are URLs that no longer lead to active or functional pages. They can significantly harm user experience and negatively impact your website’s SEO performance.
What Are the XML Sitemaps Best Practices?
Now that you have learned everything about XML, let’s look at some practices you can follow when creating an XML sitemap.
Include only crucial URLs
List only the most important, unique pages to prevent overloading search engines with irrelevant content.
Use absolute URLs
Make sure to use full URLs to ensure proper indexing.
Keep it under 50,000 URLs
A single sitemap file can only contain up to 50,000 URLs, but you can split large sitemaps into multiple files for better performance.
Following these practices ensures a smoother crawling and indexing process, contributing to better SEO outcomes.
What Are the HTML Sitemaps Best Practices?
An HTML sitemap is equally essential in improving user navigation and search engine indexing. By following these practices, you can ensure that your sitemap effectively guides visitors and search engine crawlers.
Keep it simple
Try maintaining a clear structure with a logical hierarchy for easy navigation.
Limit the number of links
Keep the number of links per page under 100 for optimal performance.
Include only important pages
Make sure to only link webpages that you want to be indexed, avoiding unnecessary or low-value content.
By adhering to these best practices, you can create an effective HTML sitemap that enhances both SEO and user experience.
What Major Issues Businesses Faces with Sitemap?
- Businesses majorly faces issues related to:
- Invalid XML Syntax
- Malformed URLs
- File Encoding Issues
- Size and URL Limits
- Incorrect Submission
- Dynamic Content Issues
- Lack of Maintenance
- Conflicting Instructions
- Technical Errors
- Plugin Conflicts
Important Points to Consider in XML Sitemap
When creating an XML sitemap for your website, there are some important factors to remember to ensure it is effective for SEO and helps search engines crawl and index your site properly.
These factors include:
- Include important pages only: One of the factors to keep in mind is that you only include essential pages in the sitemap, such as main pages, blog posts, or landing pages.
- Use correct URL formatting: Remember that each URL in the sitemap should be correctly formatted with full URLs, and the canonical version of the URL should be followed. Accurate URL formatting in sitemaps ensures that users and search engines are directed to the correct content, minimizing crawl errors.
Limit URL Count: Remember that a single XML sitemap should not exceed 50,000 URLs or 50MB in size. If your site exceeds this figure, you can create multiple sitemaps.
- Update Regularly: Always keep your website’s sitemaps updated.
With these key points, you can ensure that your XML sitemap is optimized for both search engine crawlers and site users, leading to improved site performance in search rankings.
Conclusion
And there you have it—a complete breakdown of sitemaps! From understanding what sitemaps are and how they function to the powerful SEO benefits they bring, we’ve covered all the essentials. Whether you’re running a sprawling website with thousands of pages or a fresh site with limited backlinks, a sitemap ensures that search engines can discover and index your content efficiently.
Ready to supercharge your website’s SEO strategy? At AONE SEO Service, recognized as the best SEO company in India, we specialize in creating and optimizing sitemaps tailored to your business needs.
Let’s take your website’s SEO to the next level—reach out today!
📧 Email us at info@aoneseoservice.com
📞 Call us at +918101118111
💻 or Contact Us to get started.
Your Website’s SEO success is just a click away!
FAQs
What is the difference between XML and HTML sitemaps?
The difference between XML and HTML sitemaps lies in their purpose and audience:
- XML sitemaps are designed for search engine crawlers, providing structured data about website URLs, update frequency, and priorities for indexing.
- On the other hand, HTML sitemaps are created for users, offering clickable lists of website pages to improve navigation and boost user experience.
Why is XML preferred over HTML?
XML is a preferred sitemap because it is specifically designed for search engines, offering a structured format that includes metadata like update frequency, last modification dates, and page priority. This makes XML more efficient for crawlers to understand and prioritize website content, whereas HTML primarily focuses on human-readable navigation.
Which sitemap is best for SEO?
Both XML and HTML sitemaps benefit SEO, but their effectiveness depends on the purpose.
XML sitemaps are best for search engines as they help crawlers discover and index all relevant pages. Whereas HTML sitemaps are more user-friendly, aiding navigation, enhancing user experience, and helping search engines better understand the site’s structure.
Why is a sitemap important for seo?
A sitemap is important for SEO because it helps search engines discover and index your website’s important pages. It ensures that even deep or less accessible pages are crawled, improving overall visibility in search results.