Table of Content
- What is the HTTP status code?
- Ranges of HTTP status codes
- What is the HTTP status code 200?
- What is HTTP status code 301?
- What is HTTP status code 302?
- HTTP status 404 code
- HTTP status code: 410
- What does HTTP status code 500 mean?
- HTTP status code 503
- Best Practices for Handling HTTP Status Codes
- Conclusion
Have you noticed codes such as 301, 401, and 503 while browsing a website? It can be confusing to crack the code and the meaning associated with the website, known as HTTP status codes.
The codes play a vital role for SEO and search engine spiders. The main goal of HTTP codes is to get a message across between clients and servers. For instance, a particular code indicates a page not found or an error in the website. To blur the border, let’s dig into detail to uncover the HTTP status code.
What is the HTTP status code?
HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. It’s a protocol used for communication and to exchange data between the server and your browser. When you visit a website, your browser sends a request to the server, providing the browser with a three-digit code called an HTTP status code in response. They use it to communicate to see if everything is okay or if anything is noticeably wrong. There are different types of HTTP status codes; understanding them is essential to minimizing downtime on your site and detecting site errors.
Every three-digit status code has a first digit that falls between 1 and 5; these are represented as 1xx or 5xx. Status codes are divided into five classes, each representing a distinct message type.
Ranges of HTTP status codes
Every HTTP response has a status code, which can be classified into five groups. Each response status code communicates general information regarding the request’s outcome.
The first digit of each HTTP response code designates one of the following five main categories:
1xx: Informational
Since the 1xx HTTP status codes are primarily intended for informative purposes, they indicate information. This class of status code consists of the status line and optional headers and is terminated by an empty line. A 1xx status code is not defined by HTTP/1.0 and thus is not a legitimate answer to an HTTP/1.0 request. They may be helpful in experimental applications that fall outside the purview of this standard.
The four principal status codes used in the 1xx series are:
100-Continue
101-Switching protocols
102-Processing
103-Early hints
2xx: Success
The 2xx HTTP status code indicates that the server has received, understood, and accepted a client’s request. The 2xx code is categorized as a successful HTTP response and signifies that the requested action has been processed. This code typically leads to a page confirming that the server has fulfilled your request. Here are the sub-categories of the 2xx status code.
200-OK
201-Created
203-Non-authoritative information
204-No Content
205-Rest Content
206-Partial Content
207-Multi-status
208-Already Reported
226-IIM Used
250-Low on storage space
3xx: Redirection
The 3xx HTTP status code states that the client needs to take additional measures to complete the request, as the target has been shifted to another location. Redirects require caution as they can harm the website’s performance, or if done incorrectly, redirects can confuse site visitors. This class of status codes is divided into eight HTTP status codes.
300-Multiple choices
301-Moved permanently
302-Found(Temporarily displaced)
303-See Other (Open other storage location)
304-Not Modified
305-Use Proxy
306-(Reserved)
307-Temporary Redirect
4xx: Client error
A 4xx error indicates that the webpage has restricted access or cannot be found. The 4xx status codes fall under the category where the error is on the client’s part. It means that the user can resolve the problem by changing the request made by the client or by providing appropriate verification. The issues that create error 4xx have no relation to the server. Following are the standard 4xx codes.
400-Bad Request
401-Unauthorized Request
402-Payment Required
403-Forbidden
404-Not Found
405-Method Not Allowed
406-Not Acceptable
407-Authentication Required
408-Request Timeout
409-Conflict
410-Gone
411-Length Required
412-Prediction Failed
413-Payload Too Large
414-URl Too Long
415-Unsupported Media Type
416-Range Not Satisfiable
417-Expectation Failed
429-Too Many Requests
451-Unavailable for Legal Reason
499-Client Close Request
5xx: Server error
Contradictory to the 4xx status code, the 5xx code denotes that the problem was caused by the server. This code class occurs when the server doesn’t support the functionality required to process a visitor’s request. You can only get the requested result when the server has been fixed. There’s a list of 5xx response codes below:
500-Internal Server Error
501-Not Implemented
502-Bad Gateway
503-Service Unavailable
504-Gateway Timeout
505-HTTP Version Not Supported
506-Variant Also Negotiates
507-Insufficient Storage
508-Loop Detected
509-Bandwith Limit Exceeded
510-Not Extended
511: Network Authentication Required
What is the HTTP status code 200?
HTTP status code 200 is a sub-category of the 2xx code. A server’s OK status response code determines a successful HTTP request from a browser (client). It signifies the successful retrieval of the requested data from the server and the discovery of the requested resource or page.
The requests that web browsers use to communicate with servers include:
A specific URL to find the resource and target server.
The request protocol. (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.)
Additional data, like client-side cookies or URL parameters,.
The HTTP status code 200 typically falls under the ‘Success’ status code category and is among the most commonly used. The 200 response code is crucial for your website, indicating that users can access your pages easily.
Apart from the 1xx and 2xx range of status codes, you need to understand correctly what other codes stand for. Let’s begin.
What is HTTP status code 301?
The HTTP status code 301 plays a significant role in SEO. It is a medium to communicate with the user browsers and search engines that the content or a page has been permanently shifted to another page, which triggers an auto-redirect to its new location.
The redirection code 301, a key focus in SEO site audits, is a great way to avoid 404 (page not found) error codes, which usually happen when the user clicks on a link that doesn’t exist anymore. This code is generally used when a website changes its domain name.
The redirection code 301, a key focus in SEO site audits, is a great way to avoid 404 (page not found) error codes, which usually happen when the user clicks on a link that doesn’t exist anymore.
One can utilize the free online tools like redirect-checker.org which lets you check the redirects and http status code easily.
For example,
If we enter http://aoneseoservice.com/ to check the status code of the page
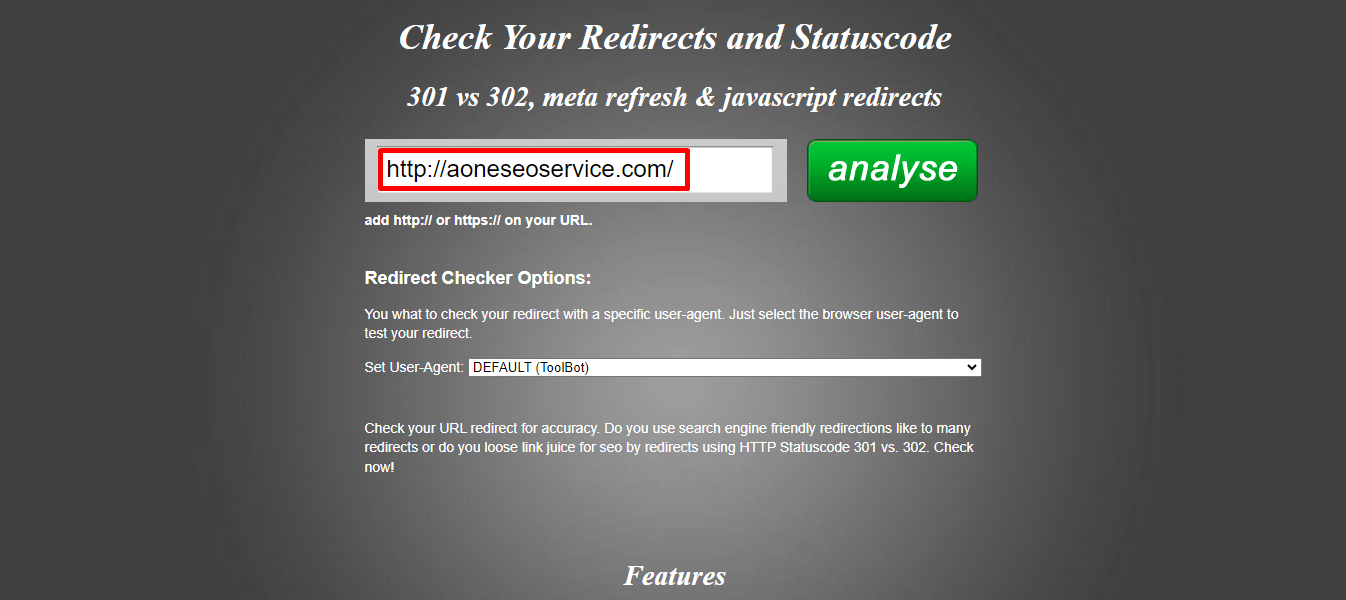

From the above screenshot, look closely that we have entered http:// (unsecure) and not https// (secure) protocol. Ideally, best SEO practice is to redirect us to https:// version using 301 http status.
Below we can see that http://aoneseoservice.com/ version is returning 301 Moved Permanently status and is redirecting to > https://aoneseoservice.com/ 301 Moved Permanently > which is redirecting again to > http://www.aoneseoservice.com/ 301 Moved Permanently > which is redirecting again to final location https://www.aoneseoservice.com/ with status code 200 OK.
From above example we see that it took three 301 redirects to reach the desired location which returns 200 OK status.
What is HTTP status code 302?
There’s a minute difference between redirect 301 and 302 response codes. The HTTP status code 301 indicates that a page is permanently moved to a new location. At the same time, a 302 redirect signifies that the page has been temporarily moved to a different location. The 302 (temporary redirection) response code redirects an access request from one URL to another. It’s intended to send the page request to the correct location without affecting the URL search engines use during page indexation.
For instance, you visit a clothing website in the United Kingdom while in Europe. A 302 redirect would send you to that site’s European version to ensure the content and currency are displayed according to your location.
Difference between 301 and 302 HTTP Redirect
Understanding the difference between 301 and 302 HTTP status codes is crucial for maintaining the integrity and performance of a website. A 301 redirect indicates a permanent move of a webpage, telling search engines that the old URL should be replaced with the new one in their index. This type of redirect passes most of the link equity (ranking power) to the redirected page, making it ideal for site restructures or permanent content relocation. In contrast, a 302 redirect signifies a temporary change, implying that the original page will eventually return. Search engines keep the original URL in their index and do not transfer the same amount of link equity.
Using a 302 redirect for a permanent move can confuse search engines, potentially harming the site’s SEO as it may split the ranking signals between the old and new URLs. Therefore, selecting the appropriate redirect type is vital for maintaining a website’s search ranking and visibility; any SEO Service company in India will go through a bunch of options before suggesting a 302 redirection.
HTTP status 404 code
The HTTP status 404 code says the server cannot find the requested source. This error occurs when the user tries to access a webpage that doesn’t exist or has a broken or dead link. A 404 response code only denotes the missing resource but doesn’t specify if it’s temporarily or permanently removed.
Pro Tip: 404 tells people that the page they’ve searched for cannot be accessed, but you can say that creatively to make them get back on track, but with some fun and sass. Replace the page Not Found with creative content. It works wonders!
How to handle 404 page for User Experience
Other than above mentioned solution, one of the major error users face is http code 404. When a user lands on a 404 error page through an internal or external link, the best practice is to turn this potentially frustrating experience into a positive one.
Firstly, the 404 page should have a friendly, clear message informing the user that the page they’re looking for can’t be found. It’s often helpful to include a touch of humor or a creative graphic to lighten the mood. Importantly, the page should offer guidance on what to do next. This can include links to the homepage, popular pages, or a search bar to encourage the user to continue exploring the site.
Additionally, providing a brief form to report the broken link can be useful for website maintenance. This approach not only improves user experience but also helps in retaining visitors, thereby minimizing the negative impact on SEO that a standard 404 error might have.

As per above screenshot we see that there is a dedicated message or visual given for pages that return with 404 http status, which is considered the good practice to have. Also, it is important to for users to have a clear path to go to.
HTTP status code: 410
HTTP status code 410 Gone means that the resource requested no longer exists because it was intentionally made unavailable permanently. Therefore, there’s a fine line between response codes 404 and 410, as 404 indicates the page has not found a temporary or permanent status, while the 410 code states that the resource doesn’t exist permanently. Sometimes, the 410 HTTP status code can be intentional and valuable to remove expired website promotions.
What does HTTP status code 500 mean?
The HTTP status code 500 is known as the Internal Server Error. It is a commonly used HTTP response code that indicates an issue on the side of the web server. Getting a 500 error code means the server has encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request made by the client or browser.
This error code is also considered the ‘catch-all’ response. The 500 Internal Server Error is a general error message covering issues that don’t fit into the existing regulations.
HTTP status code 503
The HTTP status code 503 Service Unavailable is a server error code that says the server is not ready to handle the request. Therefore, the website won’t be reached. The common causes of 503 errors include a website being too busy or under maintenance or any other reasons requiring closer analysis.
However, it is considered a generic error, so it can be challenging to gauge the exact reasons for this error. When your site experiences 503, visitors encounter a 503 response code and land on an error page.
Best Practices for Handling HTTP Status Codes
Implement the following best practices to handle HTTP status codes.
Utilize appropriate status codes
Based on the response type, select the proper HTTP status code for every answer. The HTTP status codes can be confusing and end up meaning entirely different errors than what they’re supposed to show, leaving search engines, browsers, and users needing clarification. For example, use 404 sources not found if the page is temporarily out of service or use 301 only for redirection.
Use standard HTTP status codes
Use standard HTTP status codes whenever feasible to ensure that the API offers a consistent and clear user experience. It is best to use custom status codes sparingly, as they can cause misunderstandings and complicate problem-solving.
Provide error details precisely
Give the customer thorough error information when an error status code is returned to aid in problem diagnosis and resolution. This can contain applicable error codes, a detailed error message, and a link to the relevant API documentation.
Document the API
To ensure developers understand the API, consider documenting it, including the HTTP status codes used and their implications.
Stay consistent
Ensure that the API uses HTTP status codes consistently so that the clients can quickly comprehend what each code means. This promotes a transparent and significant user experience through the API.
Conclusion
HTTP status codes are pivotal in the web ecosystem, serving as a communicative signal between browsers and servers. Web developers and SEO professionals must understand these codes, as they directly influence search engine rankings and the user experience. By promptly resolving errors and optimizing for user-friendly codes, websites can strengthen their online presence and enhance their SEO performance. To ensure your website is optimized to the fullest, consider partnering with AOne SEO Service – best SEO company. Our expert team is dedicated to helping you navigate the complexities of HTTP status codes, ensuring your site achieves its highest potential in search engine rankings. Contact us today to learn how we can elevate your website’s performance.